Rondos and positional training are fundamental components of modern football coaching. These exercises enhance players’ technical ability, decision-making, and tactical awareness while reinforcing team principles in possession-based play. By integrating these drills into training sessions, coaches can develop a more structured and efficient team capable of dominating possession and controlling games.
What Are Rondos?
Rondos are small-sided possession drills where a group of players attempts to keep the ball while one or more defenders try to win it back. The setup can vary in size, number of players, and rules, but the core principle remains the same: maintaining possession under pressure.
Benefits of Rondos
Rondos offer numerous benefits that make them a staple in elite football training programs.
- Technical Development: Players improve their passing, receiving, and first-touch ability under pressure. The repetition of these actions in tight spaces helps refine their control and execution of technical skills.
- Decision-Making: Quick passing and movement require players to assess their options rapidly. They must constantly scan their surroundings, anticipate defensive actions, and make split-second decisions.
- Tactical Awareness: Players learn to recognize space, angles, and when to support teammates. They develop an understanding of positional relationships and learn how to create passing triangles and overloads.
- Pressing and Defensive Skills: Defenders improve their ability to anticipate passes and press effectively. The offensive team, meanwhile, learns how to deal with pressure and retain possession.
- Cognitive Development: Rondos enhance cognitive functions such as perception, attention, and working memory, which are essential for high-level football performance.
Different Types of Rondos
While the classic 4v2 rondo is widely known, there are various types of rondos that serve different training objectives.
4v2 Rondos
One of the most common and fundamental rondos, the 4v2 setup involves four players keeping possession against two pressing defenders. This setup helps improve short passing, quick decision-making, and defensive pressing skills.
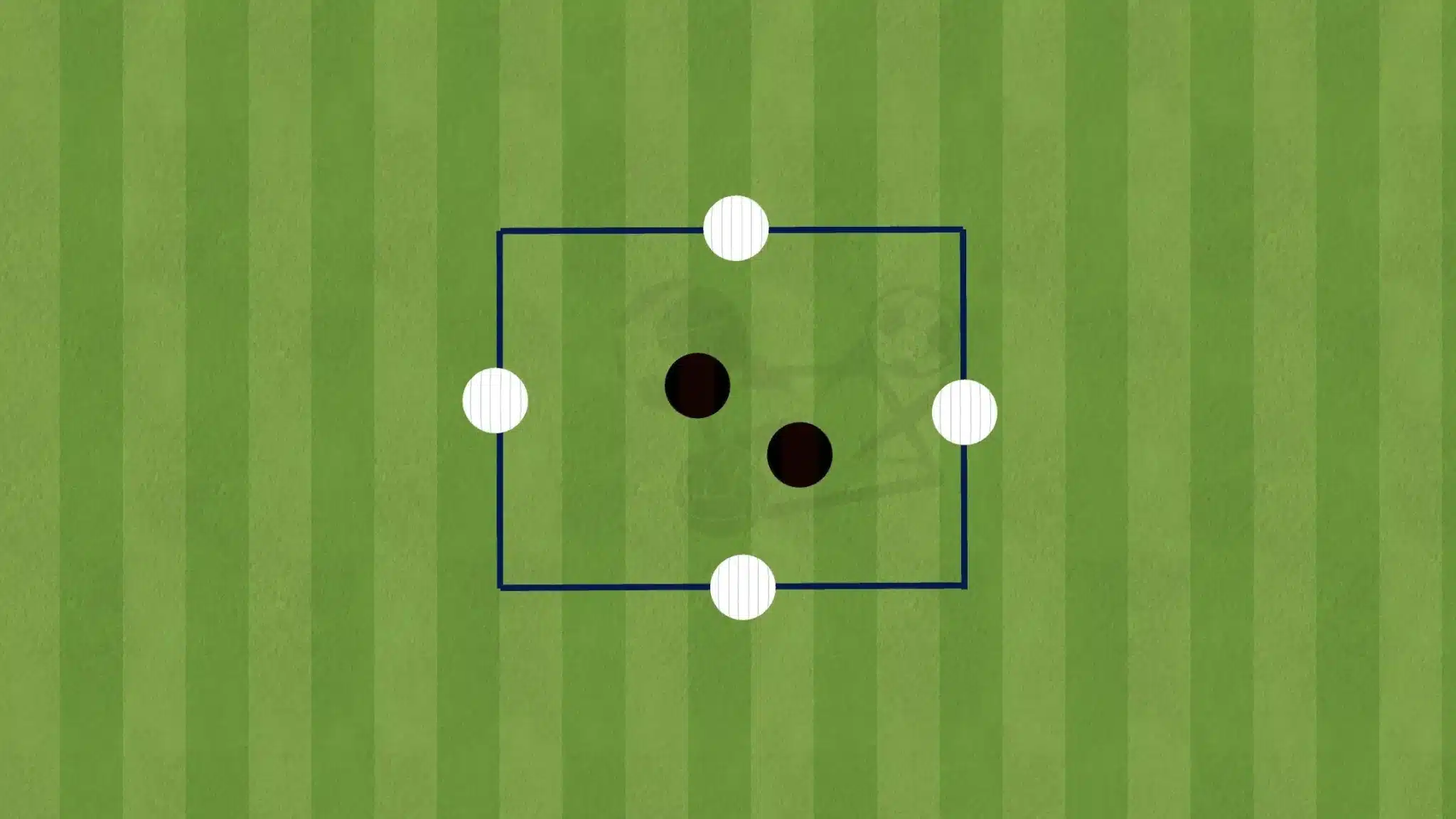
5v2 or 6v3 Rondos
Expanding the number of players in possession creates a more complex rondo that simulates real-game situations. The extra players allow for more ball circulation and require the defenders to coordinate their pressing more effectively.
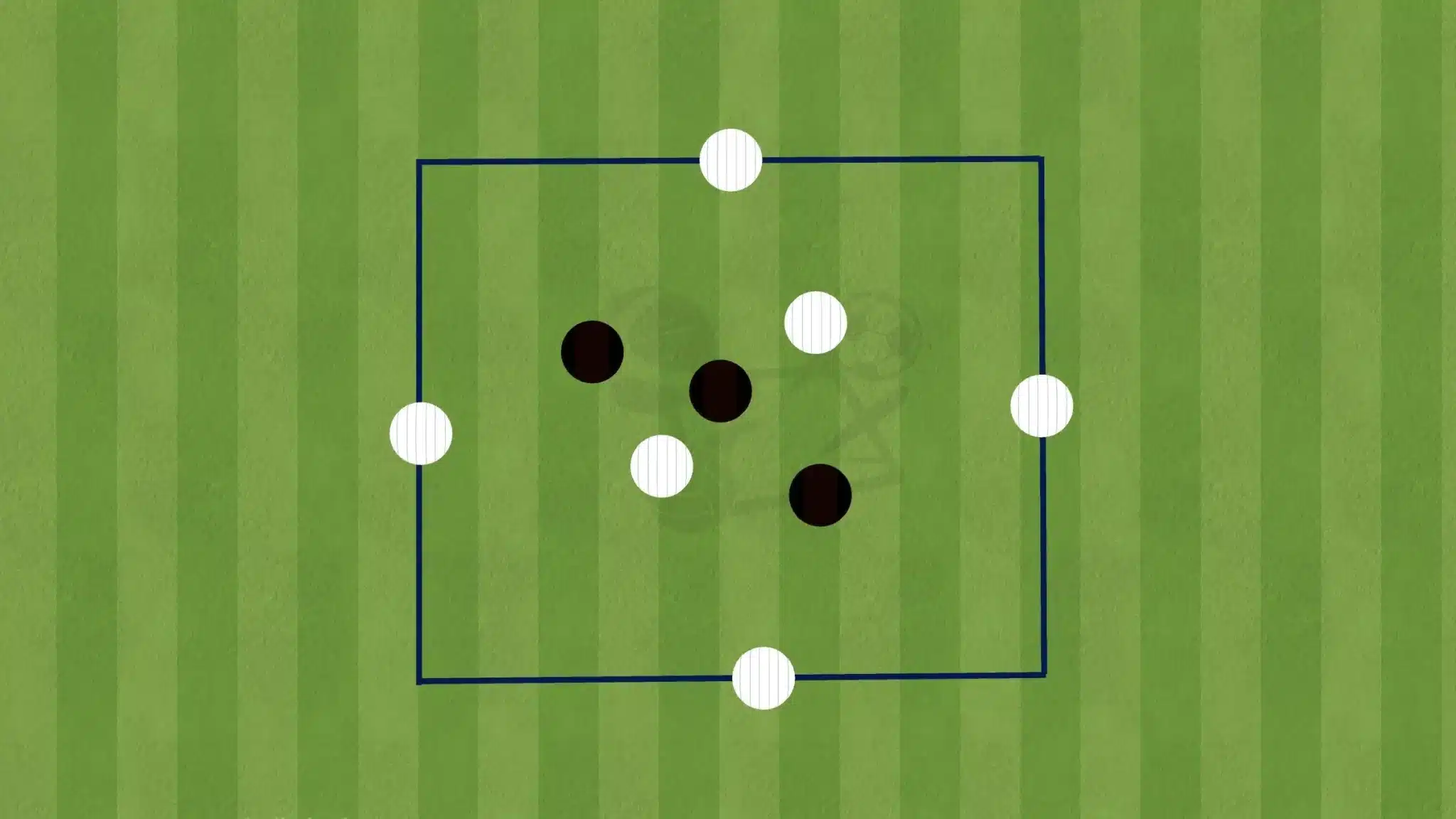
Positional Rondos (8v4, 6v3, etc.)
Positional rondos introduce game-like structures where players take up their usual match-day positions. For example, an 8v4 rondo can mimic a team’s midfield structure, involving fullbacks, central midfielders, and wingers in specific passing patterns.
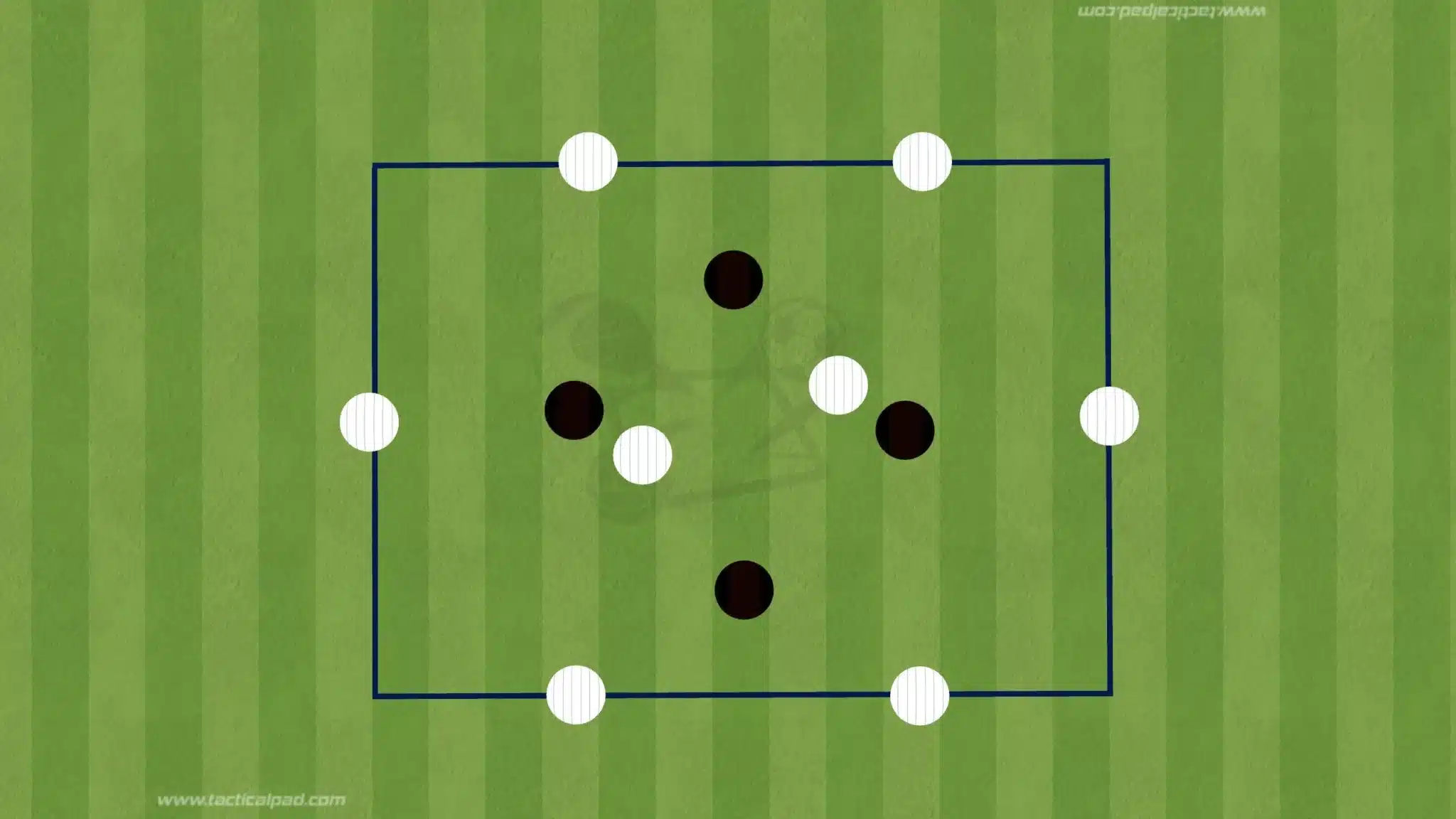
Directional Rondos
Unlike traditional rondos, which are typically contained within a small area, directional rondos involve playing toward specific target zones or goals, simulating how teams progress the ball through midfield and break opposition lines.
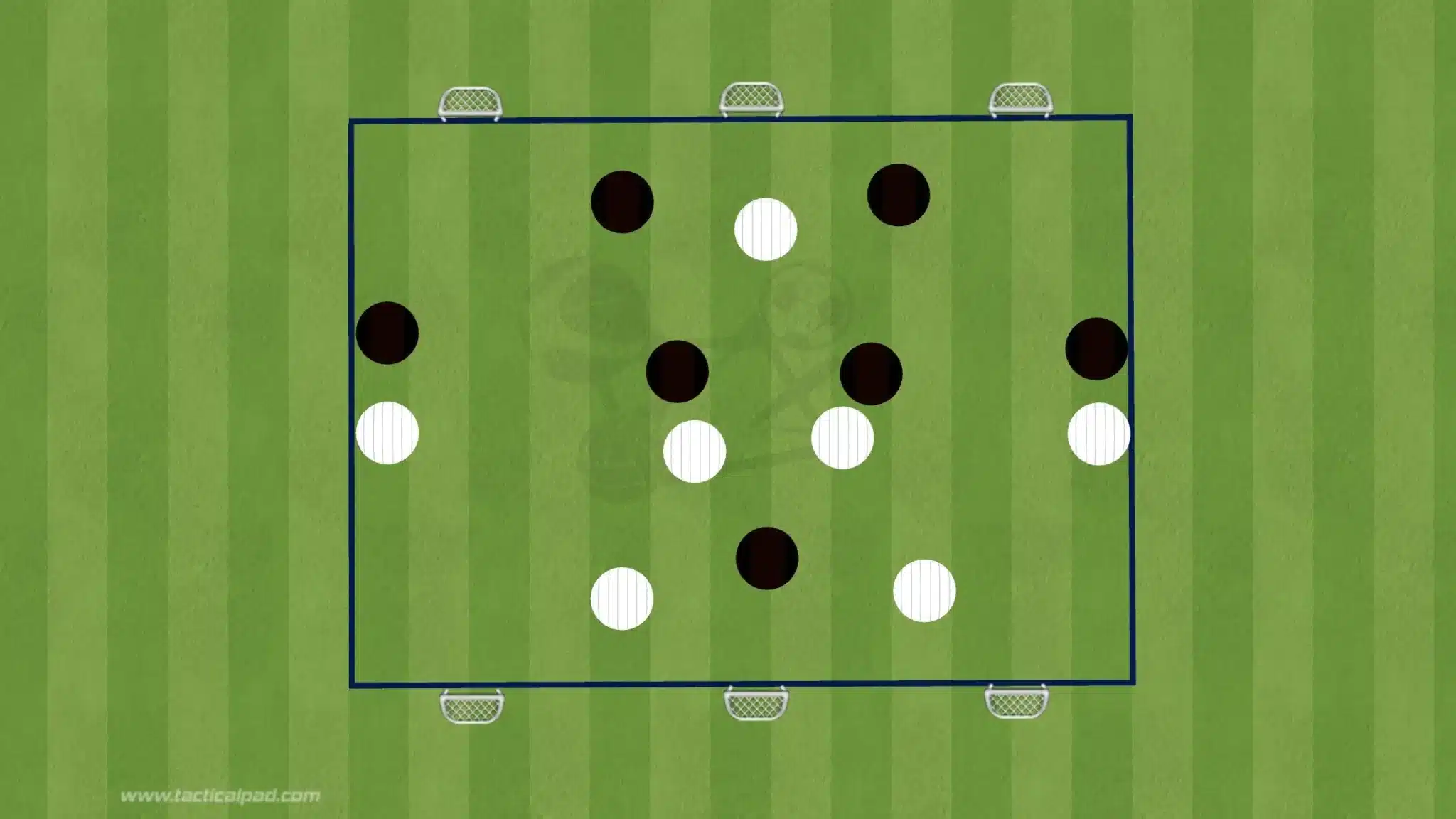
Tactical Rondos
Tactical rondos incorporate pre-defined movements and patterns that align with a team’s tactical philosophy. For instance, a team that focuses on short passing and combination play may include rondos that emphasize quick one-twos and third-man combinations.
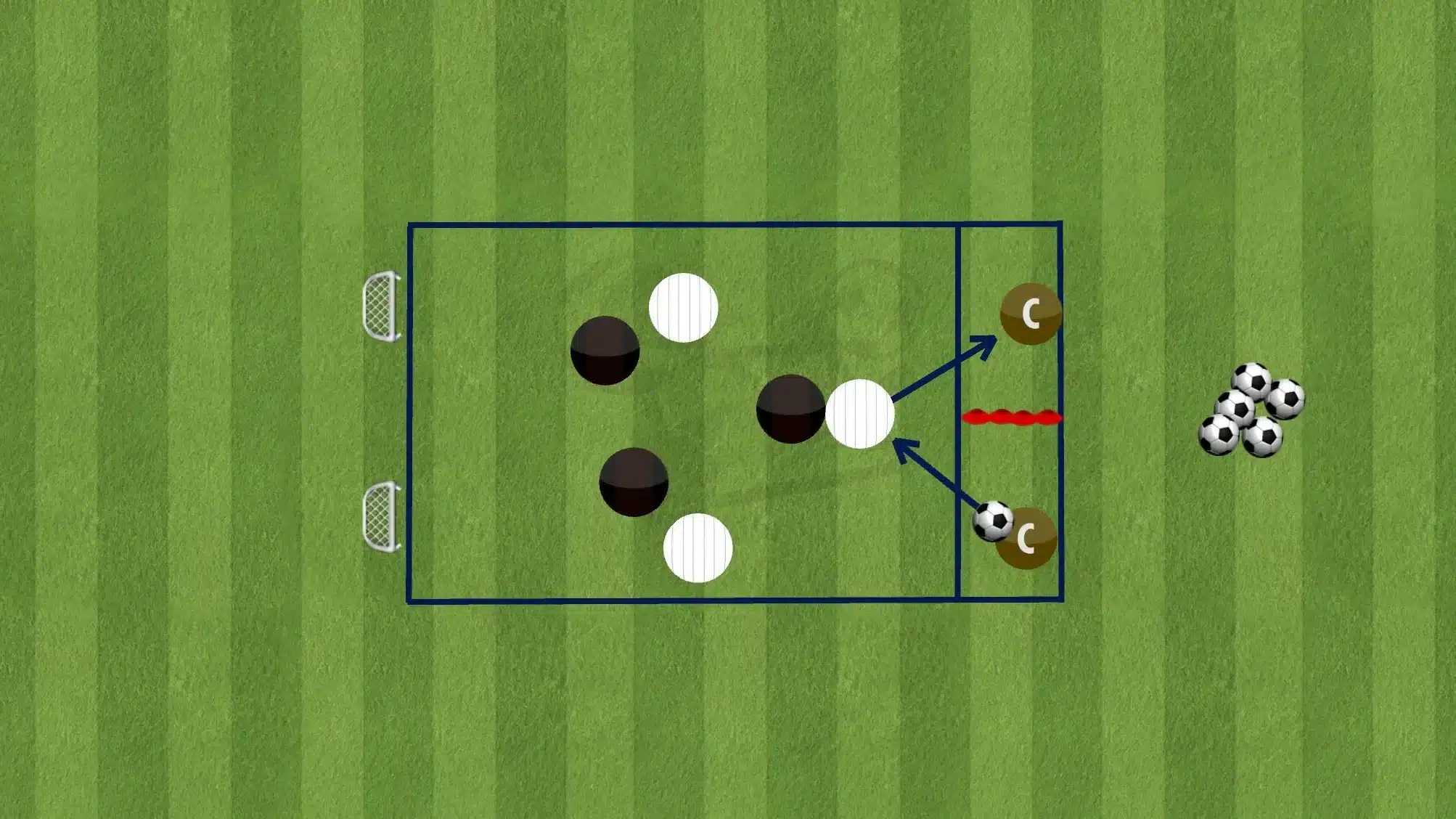
Positional Training in Football
Positional training focuses on structuring a team’s play based on designated roles and responsibilities within the system. Unlike free-play drills, positional training emphasizes movements, decision-making, and spatial awareness in relation to teammates and opponents.
Key Aspects of Positional Training
- Spatial Occupation: Players learn to position themselves optimally to create passing lanes and stretch the opposition. Proper positioning ensures that a team maintains balance and fluidity in its attacking and defensive transitions.
- Team Structure: Emphasizes maintaining shape and balance to facilitate fluid ball circulation. A well-structured team can dictate the tempo of a game and minimize defensive vulnerabilities.
- Role-Specific Movements: Players understand their positional responsibilities within the tactical framework. Each player’s movements are trained in alignment with their role in the team’s overall game model.
- Transitions: Enhances players’ reactions during attacking and defensive transitions. Quick, well-rehearsed movements help teams exploit counterattacking opportunities while also improving defensive recovery when possession is lost.
Combining Rondos with Positional Training
Rondos serve as a foundation for positional play. By integrating these drills into training sessions, coaches can reinforce principles of positional play in a dynamic, game-like environment.
For instance, rondos can be structured to mirror formations, replicating real-game scenarios where players must retain possession and break defensive lines. When applied effectively, these drills help players internalize patterns of play that they will use during competitive matches.
Positional Rondos in Tactical Systems
Coaches can design rondos that align with specific tactical frameworks.
- 1-4-3-3 Positional Rondo: Involves wingers, fullbacks, and midfielders working in a rondo setup to replicate in-game passing patterns.
- 1-3-5-2 Positional Rondo: Focuses on the midfield three and wing-backs maintaining possession and linking play between the defensive and attacking units.
- High-Pressing Rondo: Simulate situations where a team must keep possession against intense pressing, teaching players how to circulate the ball quickly under pressure.
Practical Applications of Rondos and Positional Training
- Warm-Up Drills: Short rondo sessions can serve as effective warm-ups before training or matches, allowing players to sharpen their touch and passing.
- Tactical Drills: Used to reinforce specific tactical concepts such as building out from the back, pressing triggers, or breaking defensive blocks.
- Game-Realistic Scenarios: These drills can be modified to include mini-goals or directional targets to simulate match-like decision-making.
- Youth Development: Young players benefit greatly from rondos as they develop fundamental technical skills and tactical understanding in an engaging environment.
Conclusion
Rondos and positional training are essential tools in modern football coaching, forming the backbone of possession-based philosophies. These drills not only develop technical and tactical qualities but also instill key footballing principles that enhance team performance.
By combining rondos with structured positional training, coaches can create a comprehensive training environment that prepares players for the demands of the game. Mastering these training drills leads to improved ball control, intelligent movement, and superior game awareness—all of which are crucial elements for success in football.
